In recent years, a new paradigm is slowly strengthening its hold in the web hosting industry the cloud. The reason behind its proliferation is its ability to solve long-standing issues faced by businesses hosted on traditional web hosting solutions like shared hosting, VPS, and dedicated server hosting.
Cloud delivers more convenient functionalities for overcoming issues like the underperformance of websites at faraway locations from the server, the slow process of resource upscaling, and paying even for unprocured resources. In this post, we will discuss what is cloud hosting and how it works, in very simple terms:
What is cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is a hosting solution that works on cloud computing technology wherein services like storage, computing, network, servers, and applications are provided to organizations via a network like the Internet. This form of hosting enables companies to consume computing resources as a utility, like electricity, thereby eliminating the need of building and maintain computing infrastructure in-house.
Benefits delivered by cloud hosting solution:
1. Pay for the resources that you use-??Cloud hosting is a low-cost hosting platform as customers are billed only for the resources which they procure. Moreover, it saves their upgradation costs too by helping them make the most of their current IT infrastructure.??
2. Instatenous allocation of resources-??This hosting setup facilitates on-demand scalability. It allows websites and businesses to add or reduce resources (bandwidth, storage, RAM, etc.) as per their business needs.??
3. Increased team collaboration and productivity- It enables employees of an organization to work on the same document by sharing files, applications, and other documents online, irrespective of the location they are working from. Thus, enabling flexible and smart working in the workplace.
4. Independence of location-??A business hosted on a cloud platform is globally accessible as cloud servers are present across the world. They are accessible from anywhere via an internet connection and with any device-desktop, laptop, or even mobile.??
5. No single point of failure- Does cloud hosting promise five-nine network uptime as it is a system of inter-connected servers? So whenever a single server or a component is unable to take the client’s request, then the other one out of the multiple servers takes over the workload of the failed server by default.??
6. Backup and disaster recovery-??Data is automatically backed up in cloud-connected servers.??
How Cloud hosting really works?
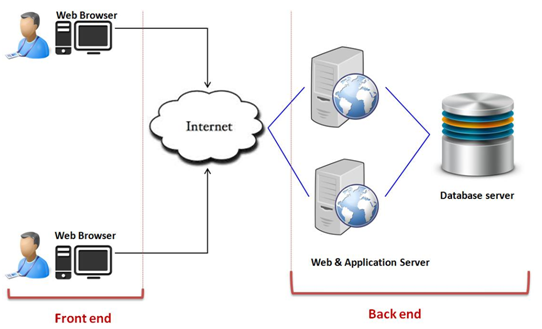
Cloud mainly consists of two components:
- Front end: Refers to the client part of cloud computing. Comprises of interfaces and applications, required to access the cloud.
It is similar to the Facebook profile which you use to interact with people.
- Back end: Refers to the cloud itself. Comprises virtual machines, servers, data storage, security mechanism, etc. Its control remains with a hosting provider. It delivers the data which we see in the front end.
Other sub-components are cloud-based delivery and network-like internet.
Cloud computing works on virtualization technology. It partitions a single physical server into multiple servers and once the server is divided, each server acts like a physical server and is capable of running an operating system and applications independently.
There are three cloud deployment models –
- Public cloud– Resources are provided by the cloud providers to the public via the Internet.
- Private cloud- Resources and infrastructure are dedicated to the use of a single organization.
- Hybrid Cloud- This model combines the goodness of the public cloud with the private cloud, thus delivering the best cloud environment.
Conclusion: The cloud is a wide network and so is a vast topic too. We???ve shared only the basics, to keep it short and sweet.